I got 4A for my AS Level in October 2013 and 4A* for my A Level in May 2014. The 4 subjects that I took were Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics and Biology. Do you want to know how to score in AS and A Level for these 4 subjects? Here, I am posting the complete tips for AS and A Level. These tips are intended for all students who are sitting for AS or A Level in May 2016 or October 2016.
AS & A Level Biology Tips:
One of the 4 subjects I took was Biology. My percentage uniform mark for Biology was 90% in AS Level and 92% in A Level. Do you want to know how to score in AS and A Level for Biology? Here, I am posting the complete tips for AS and A Level Biology.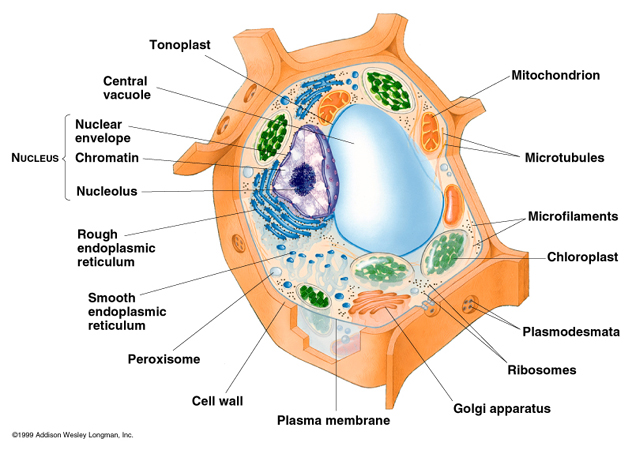
1. Studying tips
- When your teacher is teaching in class, pay attention to what your teacher says. Make sure you understand everything taught by your teacher. If you do not understand anything, ask your teacher or friends.
- You need notes or reference books that are complete.
- For AS, I recommend you to use my notes. You can download my notes here.
- For A2, I recommend you to use this reference book:
Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology, by C. J. Clegg (Hachette UK) - When studying a chapter, read through all the explanations in my notes or in the reference book sentence by sentence. Make sure that you truly understand each sentence before moving on to the next sentence. Certain topics may require understanding of earlier topics, so make sure you understand those topics. You should also try to relate them to what your teacher had taught in college or school.
- You should be actively involved in all experiments carried out in college or school because this can help improve your practical skills which are essential for Paper 3 and Paper 5.
- Then, you have to remember everything that you understood. You can memorise the sentences in my notes or in the reference book, or you can also create your own sentences that have the same meaning and memorise them. If you create your own sentences, make sure that you do not change the original meaning, do not leave out any important points and do not change the important keywords and scientific terms. However, do not just memorise without understanding. Once you have understood, it will be quite easy to remember and you will be unlikely to forget any of the points.
- For certain facts, there may be no explanation for them so it is not possible to understand them. In that case, you have to remember and memorise those facts.
- You have to regularly revise every topics again and again. When revising, go through all the explanation and facts in my notes or in the reference book. Make sure that you do not forget anything that you have understood previously. Regular and repeated revision will help you to remember all the explanation and facts for a long time.
- When you have understood all topics, you have to do past year A Level questions. They are available on the internet. After doing the questions, refer to the mark scheme and do self marking. The mark schemes can usually be found on the same website as the past year questions.
- You should understand how the mark schemes are used. In the mark schemes for Biology, most marks are independent of any other marks, which means that they can be scored without other marks also being scored, unless otherwise stated by the mark scheme. If any biological term is underlined or highlighted, it means that the exact term must be used in the answer and no other term is acceptable even if the meaning is the same, but grammatical variants of the term is accepted. If any non-biological term is underlined or highlighted, it means that either the exact term or other terms with the same meaning must be used in the answer. If any words are placed in brackets, it means that the words need not be present in the answer for the mark to be scored. In the mark schemes, A means accept, I means ignore while R means reject.
- When doing revision before exam, you should first go through the subtopics that you think is more difficult or that you may have forgotten. Then, go through other topics as well if possible.
- To prepare for Biology Paper 3 and Paper 5, you should go through all the past year questions and the mark schemes. Find out how every question is marked and which points need to be included in the answers. The pattern of questions set is similar for every year and you should familiarise yourself with the pattern. Usually, the same type of questions will have similar mark scheme, so this can help you when answering exam questions. You should remember the answers for questions that are common.
2. Paper 1
- Read the question and all the options carefully. Write any rough workings on the question paper if you need to. Cancel off the options that you consider as definitely wrong. Then, choose the most suitable answer among the options.3. Paper 2 and Paper 4
- Paper 2 and Paper 4 Section A consists of structured questions where you must answer all questions while Paper 4 Section B consists of 2 essay questions where you can choose any one of them. You can answer both questions in Paper 4 Section B if you have time. The examiner will mark your answers for both questions and choose the one where you score higher marks.
- When answering, read the question and all information given carefully. Make sure that you know what the question is asking for. Answer the questions based on your knowledge and understanding on the relevant topic in Biology. Certain questions may test you on more than one topics. For some questions, you may have to apply what you have learnt in Biology in order to answer them. You have to think carefully and relate the question to what you have learnt. You may also be asked to give your own opinions.
- When writing your answer, you can use the same or similar words or sentences as those in my notes or in the reference books if possible. However, sometimes you may need to make some changes in order to suit the question. You can also answer in your own sentences that have the same meaning. If the question asks on something that is not in my notes and the reference books (the question requires you to apply what you have learnt in Biology or give your own opinion), then you have to answer in your own sentences. For all questions, your answer must be specific and not too general. Give the most suitable answer according to the question.
- You should use the correct biological terms in your answer. Do not replace them with other terms that are inappropriate, even if their meaning are the same. You should spell all biological terms correctly. If you can't do so, try to spell it in such a way where it sounds the same as the actual term when read out. Marks are usually not deducted for spelling errors in biological terms as long as it still sounds the same and that it is not easily confused with other terms. If you spell a non-biological term wrongly or if you make grammatical errors in your answer, marks will not be deducted for as long as the examiner can understand what you are writing. You are allowed to use suitable short forms in your answer, such as formula for chemical substances and symbols for units of physical quantities.
- It is not compulsory to answer in continuous writing form. You are allowed to answer in table form, point form or other suitable forms. In suitable cases, you can also use diagrams, equations or graphs in your answer.
- When answering questions on calculation, you should show all workings. You should not skip any important steps. You must also write the correct unit for the final answer if it is not provided. The number of marks allocated for the question usually shows the amount of working needed. 1 mark will be given for each important step and the final answer. Correct answer without working usually scores only 1 mark. If your final answer is wrong but some of your working is correct, you may still be given some marks. You are not allowed to write extra solutions or answers. If you do so and any of the answers or solutions is wrong, marks will be deducted. For a calculation question which requires you to use your answer from the previous question, even if your answer for the previous question is wrong and you use it for this question causing your answer for this question to be wrong, usually you will still get full marks for this question as long as your calculation for this question is correct. This is known as 'error carried forward'.
- When describing numerical data shown in a graph or table, you should quote suitable figures together with their units from the graph or table. For graph, each set of figure that you quote should include both the x value and y value and you should quote the figures accurate to half a small square.
- For questions that require explanation or description, your answer must be very detailed. You are advised to answer in complete sentences so that your answer can be easily understood. The number of marks allocated for the question usually shows the number of points needed in your answer. 1 mark is given for each correct point. Do not miss out any important points in your answer. You are allowed to write extra points in your answer, but you must be careful not to write any points that contradict one another. Marks will only be given for the correct points. For points that are not acceptable, whether they contain wrong facts or not, no mark will be given or deducted. However, for points that contradict one another, no mark will be given for both the points, even if one of them is correct. You are advised to write extra points if you are not completely sure of what the question is asking for.
- For questions that do not require explanation or description, write the answer straight away. You need not answer in complete sentences. The number of marks allocated for the question usually shows the number of answers needed. You are allowed to write extra answers, but you must be careful not to write answers that contradict one another. Marks will only be given for the correct answers. For answers that are not acceptable, whether they contain wrong facts or not, no mark will be given or deducted. However, for answers that contradict one another, no mark will be given for both the answers, even if one of them is correct.
- When drawing diagrams, make sure that all important details are included in the diagram you draw. You have to label correctly all parts in the diagram. Your diagram should be clear and neat.
4. Paper 3
- During the test, read the question and all information given carefully. Make sure that you understand the experiment given. Certain parts of the question require you to record the readings from the experiment in a table. You should draw the tables before carrying out the experiment so that you can record your readings in the table straight away during the experiment. Then, carry out the experiment by following the steps given in the question exactly. You need to apply your Biology practical skills when carrying out the experiment.
- Certain questions may require your knowledge and understanding in Biology to answer them. You may also need to give your own opinions. Your answer must be specific and not too general. Give the most suitable answer according to the question.
- When recording readings from an measuring instrument, the number of decimal places used should be equal to half of the smallest division of scale of the instrument (For example, if the instrument's smallest division of scale is 0.1, you should record the reading to the nearest 0.05, which is 2 decimal places.) For digital instruments (except digital stopwatch), the number of decimal places used should be the same as that shown on the display. The reading should be recorded to the nearest 1s for stopwatch (both analogue and digital). In all cases, do not give more or less number of decimal places. You must also write the correct units.
- When plotting graph, draw both the horizontal and vertical axis on the graph paper correctly. You should plot the independent variable on the x-axis and dependent variable on the y-axis. Label both axis correctly and state the unit (if any). Use a suitable scale for both axis and do not use any odd scales such as 3:10. Both the x-axis and y-axis need not start from 0 (unless otherwise stated by the question). The scales should be chosen such that the graph cover at least half of the graph paper. For line graphs, the markings on the scales should be 2cm apart, plot all points on the graph accurate to half a small square and the diameter of each point should not be larger than half a small square, then draw a curve or straight line that passes through all points on the graph if it is possible to do so, or if it is not possible, you can just use straight lines to join them point-to-point, and in all cases never extrapolate the line. For bar charts, draw blocks with equal width accurate to half a small square, where there must be space between the blocks and the distance between adjacent blocks should be equal, then label every block.
- For questions on microscopy, you will be required to draw plan diagrams and high power drawings. For all drawings, use pencil to draw, draw as big as possible without drawing over the text of the question and leave enough space for labels, ensure that the lines you draw are thin, single, unbroken, clear & continuous and never shade or colour. When drawing plan diagrams, use low power objective lens of the microscope, show the outlines of the tissues, ensure that the proportions of tissues in the diagram you draw is the same as what you see and do not include drawings of cells. When drawing high power drawings, use high power objective lens of the microscope, draw only what the question asks, show the outlines of the cells, ensure that the proportions of cells in the diagram you draw is the same as what you see, show the cell walls of plant cells as double lines and where plant cells touch there should be 3 lines and show any contents of cells that you can see which may be nucleus, chloroplasts, vacuoles or others. Label your diagram if required by the question. Use a ruler to draw the labelling lines.
- For any questions involving calculation, the number of significant figures of your answer should be equal to the number of significant figures of the raw value used in the calculation with the least number of significant figures. You should show all workings and do not skip any important steps. You must also write the correct unit for the final answer if it is not provided. You are not allowed to write extra solutions or answers. If you do so and any of the answers or solutions is wrong, marks will be deducted. For a calculation question which requires you to use your answer from the previous question, even if your answer for the previous question is wrong and you use it for this question causing your answer for this question to be wrong, usually you will still get full marks for this question as long as your calculation for this question is correct. This is known as 'error carried forward'.
- For questions that require explanation or description, your answer must be very detailed. You are advised to answer in complete sentences so that your answer can be easily understood. The number of marks allocated for the question usually shows the number of points needed in your answer. 1 mark is given for each correct point. Do not miss out any important points in your answer. You are allowed to write extra points in your answer, but you must be careful not to write any points that contradict one another. Marks will only be given for the correct points. For points that are not acceptable, whether they contain wrong facts or not, no mark will be given or deducted. However, for points that contradict one another, no mark will be given for both the points, even if one of them is correct. You are advised to write extra points if you are not completely sure of what the question is asking for.
- For questions that do not require explanation or description, write the answer straight away. You need not answer in complete sentences. The number of marks allocated for the question usually shows the number of answers needed. You are allowed to write extra answers, but you must be careful not to write answers that contradict one another. Marks will only be given for the correct answers. For answers that are not acceptable, whether they contain wrong facts or not, no mark will be given or deducted. However, for answers that contradict one another, no mark will be given for both the answers, even if one of them is correct.
- When drawing diagrams, make sure that all important details are included in the diagram you draw. You have to label correctly all parts in the diagram. Your diagram should be clear and neat.
- For all questions, you should use the correct experimental and biological terms in your answer. Do not replace them with other terms that are inappropriate, even if their meaning are the same. You should spell all experimental and biological terms correctly. If you can't do so, try to spell it in such a way where it sounds the same as the actual term when read out. Marks are usually not deducted for spelling errors in experimental and biological terms as long as it still sounds the same and that it is not easily confused with other terms. If you spell other terms wrongly or if you make grammatical errors in your answer, marks will not be deducted for as long as the examiner can understand what you are writing. You are allowed to use suitable short forms in your answer, such as formula for chemical substances and symbols for units of physical quantities.
5. Paper 5
- When answering, read the question and all information given carefully. Make sure that you understand the experiment given and know what the question is asking for. Answer the questions based on the experiment and its observations and results. You may need to apply your Biology experimental skills to answer some questions. Certain questions may require your knowledge and understanding in Biology to answer them. You may also need to give your own opinions. For all questions, your answer must be specific and not too general. Give the most suitable answer according to the question.
- You should use the correct biological and experimental terms in your answer. Do not replace them with other terms that are inappropriate, even if their meaning are the same. You should spell all biological and experimental terms correctly. If you can't do so, try to spell it in such a way where it sounds the same as the actual term when read out. Marks are usually not deducted for spelling errors in biological and experimental terms as long as it still sounds the same and that it is not easily confused with other terms. If you spell other terms wrongly or if you make grammatical errors in your answer, marks will not be deducted for as long as the examiner can understand what you are writing. You are allowed to use suitable short forms in your answer, such as formula for chemical substances and symbols for units of physical quantities.
- It is not compulsory to answer in continuous writing form. You are allowed to answer in table form, point form or other suitable forms. In suitable cases, you can also use diagrams, equations or graphs in your answer.
- For any questions involving calculation, the number of significant figures of your answer should be equal to the number of significant figures of the raw value used in the calculation with the least number of significant figures. You should show all workings and do not skip any important steps. You must also write the correct unit for the final answer if it is not provided. You are not allowed to write extra solutions or answers. If you do so and any of the answers or solutions is wrong, marks will be deducted. For a calculation question which requires you to use your answer from the previous question, even if your answer for the previous question is wrong and you use it for this question causing your answer for this question to be wrong, usually you will still get full marks for this question as long as your calculation for this question is correct. This is known as 'error carried forward'.
- For questions that require explanation or description, your answer must be very detailed. You are advised to answer in complete sentences so that your answer can be easily understood. The number of marks allocated for the question usually shows the number of points needed in your answer. 1 mark is given for each correct point. Do not miss out any important points in your answer. You are allowed to write extra points in your answer, but you must be careful not to write any points that contradict one another. Marks will only be given for the correct points. For points that are not acceptable, whether they contain wrong facts or not, no mark will be given or deducted. However, for points that contradict one another, no mark will be given for both the points, even if one of them is correct. You are advised to write extra points if you are not completely sure of what the question is asking for.
- For questions that do not require explanation or description, write the answer straight away. You need not answer in complete sentences. The number of marks allocated for the question usually shows the number of answers needed. You are allowed to write extra answers, but you must be careful not to write answers that contradict one another. Marks will only be given for the correct answers. For answers that are not acceptable, whether they contain wrong facts or not, no mark will be given or deducted. However, for answers that contradict one another, no mark will be given for both the answers, even if one of them is correct.
- When drawing diagrams, make sure that all important details are included in the diagram you draw. You have to label correctly all parts in the diagram. Your diagram should be clear and neat.
- When plotting graph, draw both the horizontal and vertical axis on the graph paper correctly. You should plot the independent variable on the x-axis and dependent variable on the y-axis. Label both axis correctly and state the unit (if any). Use a suitable scale for both axis and do not use any odd scales such as 3:10. Both the x-axis and y-axis need not start from 0 (unless otherwise stated by the question). The scales should be chosen such that the graph cover at least half of the graph paper. For line graphs, the markings on the scales should be 2cm apart, plot all points on the graph accurate to half a small square and the diameter of each point should not be larger than half a small square, then draw a curve or straight line that passes through all points on the graph if it is possible to do so, or if it is not possible, you can just use straight lines to join them point-to-point, and in all cases never extrapolate the line. For bar charts, draw blocks with equal width accurate to half a small square, where there must be space between the blocks and the distance between adjacent blocks should be equal, then label every block. After that, draw the error bars based on the standard error or standard deviation if required by the question.
- For the question on planning experiment, when writing the procedure, you must include the steps to change the independent variable, measure the dependent variable and control the constant variable, as well as other steps required to set up the apparatus. You should also state the potential safety hazards when carrying out the experiment and the ways to avoid them. If there is no significant safety hazard, just state in your answer 'This is a low risk experiment'. Besides, you have to state the ways to improve the reliability of the experiment such as repeating the experiment and calculating the mean or identifying anomalies. In the procedure, you should state the amount and concentration of the substances used. You are advised to answer in complete sentences so that your answer can be easily understood. You do not need to draw the diagram of set-up apparatus.
Related Post: Revision Notes for CIE AS & A Level Subjects (New 2016 Syllabus)
Daniel Lim Jhao Jian, 20, speaks English, Mandarin and Malay. His hobbies are surfing the internet, watching television and reading. His ambition is to be a doctor.
Daniel was born in Subang Jaya, Selangor, but he grew up in Kulim, Kedah. He lived in Kulim with his grandparents for 17 years. His primary school was SRJK(C) Chong Cheng while his secondary school was SMK Sultan Badlishah. After completing secondary school, he moved to Subang Jaya and he studied Cambridge A Level at Taylor's College Subang Jaya for 1.5 years. Currently, he is living in Johor Bahru, Johor and studying 2nd year of Medicine course at Newcastle University Medicine Malaysia.
These tips were first posted at Daniel's blog.
► Read more on Exam Tips: How to Score A in CIE AS and A Level Biology




